204 results
Impact of complete revascularisation in relation to left ventricular function in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and multivessel disease: a post hoc analysis of the COMPLETE randomised trial
05 Feb 2026
This study represents a prespecified subgroup analysis of the COMPLETE randomised trial, a large, international, randomised controlled study comparing a strategy of complete revascularisation with culprit-only percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and multivessel coronary artery disease (MVD).
The present...

Reviewer

Reviewer

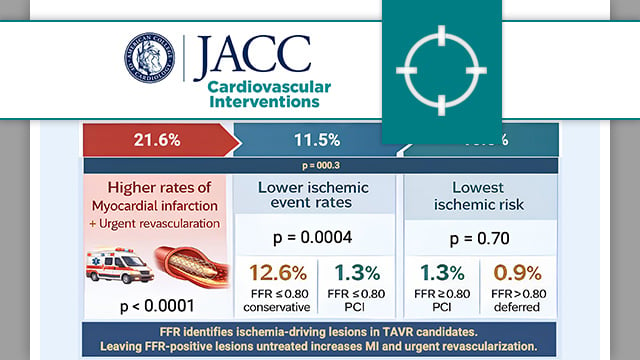
Fractional flow reserve to guide revascularisation in patients with coronary artery disease undergoing TAVR
07 Jan 2026
The present analysis compared major adverse cardiac events in patients with significant coronary stenosis (FFR ≤ 0.80 or visual stenosis ≥ 90 %) versus those with non-significant stenosis (FFR > 0.80).

Reviewer

Reviewer
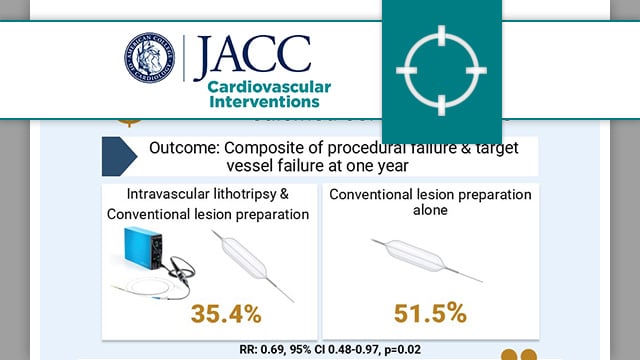
Balloon lithotripsy added to conventional preparation before stent implantation in severely calcified coronary lesions
06 Jan 2026
In patients with severely calcified coronary lesions undergoing PCI, the BALI trial evaluated the benefit of the addition of intravascular lithotripsy to conventional lesion preparation on the composite endpoint of procedural failure and target vessel failure.

Reviewer
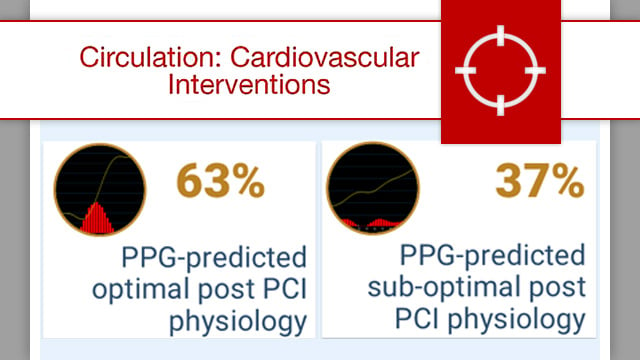
Impact of pullback pressure gradient on clinical outcomes after percutaneous coronary interventions
02 Dec 2025
While FFR traditionally reflects the severity of a lesion at a fixed location, PPG incorporates the pullback profile, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of disease distribution.

Reviewer

Reviewer
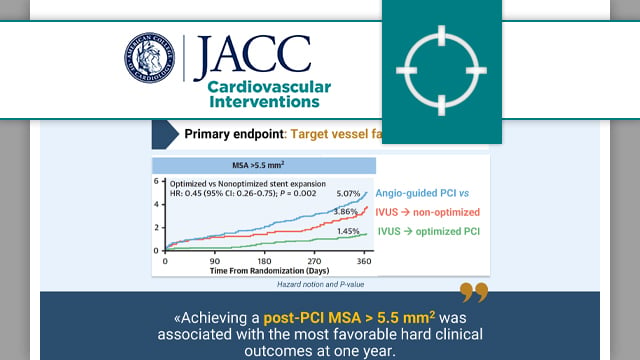
Validation of intravascular ultrasound-defined optimal stent expansion criteria for favorable 1-year clinical outcomes
17 Nov 2025
This individual patient data analysis of the three largest RCTs evaluating IVUS-guided stent optimisation showed that an MSA > 5.5 mm2 was associated with reduced TVF at one year.

Reviewer

Reviewer
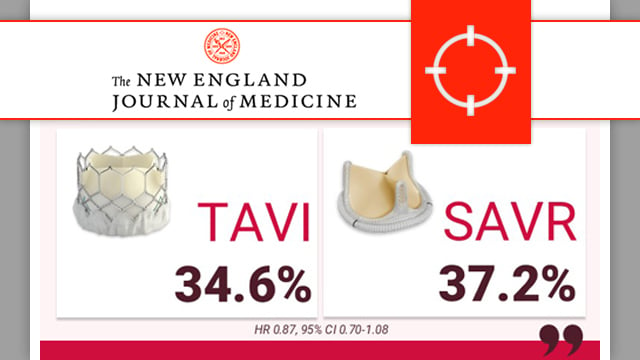
PARTNER 3: transcatheter or surgical aortic-valve replacement in low-risk patients at 7 years
14 Nov 2025
At 7 years, low-risk patients affected by severe symptomatic aortic valve stenosis 1:1 randomly treated by SAPIEN 3 TAVI or surgery showed similar clinical outcomes and late valve durability

Reviewer

Reviewer
CLEAR-IE: outcomes of percutaneous mechanical aspiration in right-sided infective endocarditis
06 Oct 2025
Can mechanical aspiration offer a safer, less invasive option for managing right-sided infective endocarditis? The CLEAR-IE registry provides valuable early insights.

Reviewer

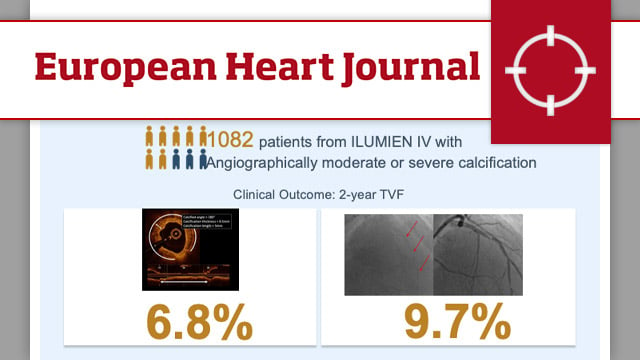
Optical coherence tomography- vs angiography-guided coronary stent implantation in calcified lesions: the ILUMIEN IV trial
28 Aug 2025
In the overall population (n = 2,114), there was a significant interaction between the effect of randomisation to OCT guidance vs angiography guidance in lesions with moderate/severe calcification (n = 1,082) vs no/mild calcification (n = 1,032) on the 2-year rate of TVF (Pinteraction = 0.01).

Reviewer
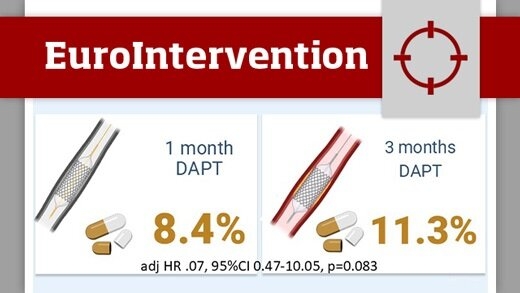
One- versus three-month DAPT after everolimus-eluting stent implantation in diabetic patients at high-bleeding risk: results from the XIENCE Short DAPT programme
17 Jun 2025
This analysis from the XIENCE Short DAPT programme compared the safety and efficacy of one-month versus three-month DAPT in high-bleeding risk patients with and without diabetes mellitus (DM) following PCI with everolimus eluting stents (EES).

Reviewer
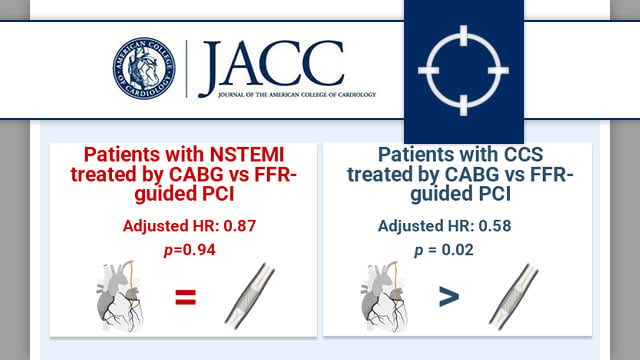
Outcomes after CABG compared with FFR-guided PCI in patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome
10 Jun 2025
This prespecified analysis of the Fractional Flow Reserve versus Angiography for Multivessel Evaluation (FAME 3) trial examined the impact on cardiovascular outcomes of treatment by CABG versus FFR-guided PCI in patients with three vessel disease (3-VD), stratified by acute (NSTEMI) or chronic coronary syndrome (CCS) presentation.

Reviewer

Reviewer