RIVER: Rivaroxaban for valvular heart disease and atrial fibrillation
Reported from ESC Congress 2023
Alex Sticchi provides his take on the results of the RIVER trial, which were presented by Pedro Gabriel Barros E Silva during the ESC 2023 congress in Amsterdam.
Rivaroxaban versus Warfarin in Patients with Bioprosthetic Valves According to Valvular Heart Disease Etiology, and Thrombotic and Bleeding Risks: Insights from the RIVER Randomized Trial

Rivaroxaban versus Warfarin in Patients with Bioprosthetic Valves According to Valvular Heart Disease Etiology, and Thrombotic and Bleeding Risks: Insights from the RIVER Randomized Trial - Designed by @Sticchi_Alex
Why this study – the rationale/objective?
The RIVER trial is a multicenter (49 Brasilian sites), investigator-initiated, randomized, open-label trial, supported by the Brazilian Ministry of Health (PROADISUS). The study randomized 1005 patients to rivaroxaban (20 mg once daily) versus (vs) dose-adjusted warfarin (target international normalized ratio, 2.0 to 3.0) in patients with atrial fibrillation and a bioprosthetic mitral valve.
The events have been adjudicated by a blinded Clinical Events Classification Committee. The Primary Endpoint was a composite of death, major CV events (stroke, TIA, valve thrombosis, systemic embolism not related to the central nervous system, or hospitalization for heart failure) or major bleeding at 12 months.
The RIVER study published in 2020 on the NEJM showed rivaroxaban was noninferior to warfarin with respect to death, major cardiovascular events, or major bleeding (N Engl J Med 2020; 383:2117-2126) in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) or flutter and a bioprosthetic mitral valve. CHA2DS2VASC and HAS-BLED scores have not been validated in patients with valvular atrial fibrillation. Moreover, the presence of rheumatic heart disease (RHD) in the RIVER trial population could have influenced the outcomes in terms of risk of bleeding (BE) and thromboembolic event (TE). About this issue, the recent INVICTUS trial (N Engl J Med 2022; 387:978-988) showed the superiority of Warfarin compared to Rivaroxaban in patients with AF and RHD (Primary Endpoint Hazard Ratio [HR] 1.25 [1.10-1.41]).
The therapeutic effect of Rivaroxaban compared to Warfarin needs to be further investigated.
This subanalysis aimed to evaluate efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban compared with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation or flutter and a bioprosthetic mitral valve according to:
- Thromboembolic and bleeding risks (including traditional and potential new risk factors such as rheumatic heart disease)
- Valvular heart disease etiology (rheumatic vs. non-rheumatic).
How was it executed? - the methodology
In this sub-analysis presented at the ESC Congress 2023, the authors developed models for BE and TE with initial selection of variables with p-values less than 0.2. They used a stepwise selection method starting from the collected variables to define the final model. The two models have been used for rheumatic and non-rheumatic etiology as well. The Valvular Heart Disease (VHD) etiology has been collected retrospectively for the most (79.9% [803 patients]). The models' performance was assessed through the ROC curve, and the separation of individuals into low-risk and high-risk categories was based on the Youden index.
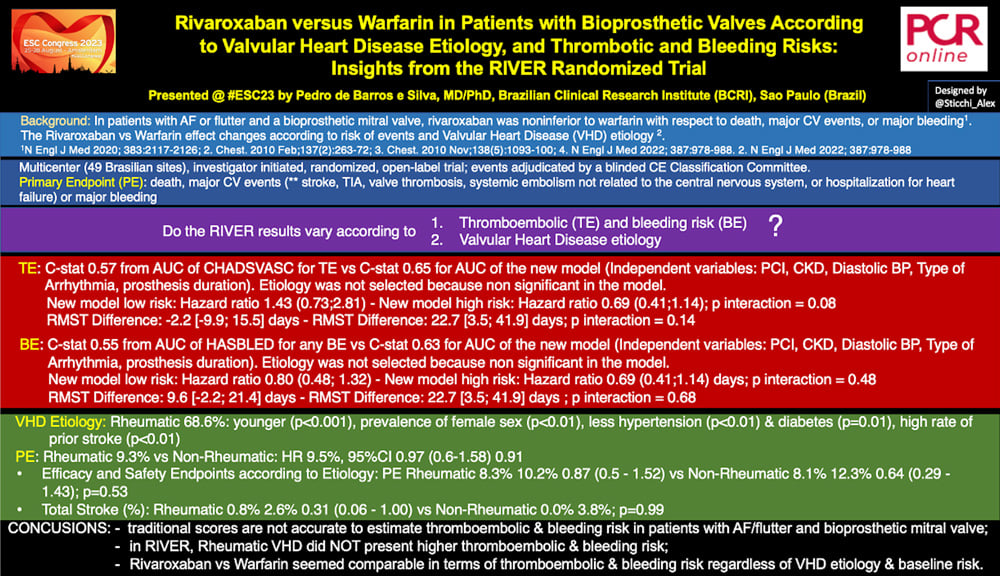
About the TE, C-stat was 0.57 from the AUC of the CHADSVASC vs C-stat 0.65 for AUC of the new model. As independent variables, the authors included PCI, CKD, Diastolic BP, Type of Arrhythmia, prosthesis duration. Etiology was not selected as an independent variable in the model and C-statistic was 0.62 forcing it into the model.
About the BE, C-stat was 0.55 from AUC of the HASBLED for any BE vs C-stat 0.63 for AUC of the new model. Independent variables associated with BE were PCI, CKD, Diastolic BP, Type of Arrhythmia and prosthesis duration. Again, etiology was not selected because it was non-significant in the model and its forcing did not improve C-stat.
Once the models were computed, they were applied stratifying the population for high and low risk in terms of TE and BE.
What is the main result?
About TE, the new model presented HR 1.43 (0.73;2.81) for the low risk, and HR 0.69 (0.41;1.14) for the high risk, p interaction = 0.08.
About BE, the new model showed an HR of 0.80 (0.48; 1.32) for the low-risk, and HR 0.69 (0.41;1.14) days for the high-risk, p interaction = 0.48.
Regarding the VHD etiology, 68.6% of the population presented RHD. These patients differed from the non-rheumatics for being younger (Age [y], mean ± SD 55.86 ± 11.5 vs 65.12 ± 10.94, p<0.01), a larger prevalence of women (69.3% vs 39.7%, p <0.01) and more comorbidities with a higher rate of prior stroke history (15.3% vs 6.8%, p <0.01).
The overall events were similar between RHD and non-RHD. The primary endpoint was 9.3% for RHD vs non-RHD, HR 0.97 (0.6-1.58), p=0.91; total stroke 1.6% for RHD vs 1.6% for non-RHD, HR 1.03 (0.32-3.35), p=0.95.
Finally, in terms of treatment effect (Efficacy and Safety Endpoints according to Etiology), there was no correlation about valve etiology, RHD vs non-RHD for the PE (Rheumatic 8.3% 10.2% 0.87 (0.5 - 1.52) vs Non-Rheumatic 8.1% 12.3% 0.64 (0.29 - 1.43); p=0.53).
The same missing interaction was shown for the individual components in both analyses.
In conclusion, among patients presenting AF or flutter and a bioprosthetic mitral valve, traditional scores did not seem accurate in estimating thromboembolic & bleeding risk. In RIVER, Rheumatic VHD did not present higher thromboembolic & bleeding risk. Rivaroxaban seemed comparable to warfarin in terms of thromboembolic & bleeding risk regardless of VHD etiology & baseline risk.
Critical reading and the relevance for clinical practice
The RIVER trial is currently the only randomized study to assess the use of new oral anticoagulation compared to warfarin in patients with mitral bioprosthesis and AF/flutter. This is an interesting new scenario, and it will be very important in the future considering the widespread use of both surgical and transcatheter bioprosthesis. We need to explore if new anticoagulants are a safe and efficacy treatment in valvular heart disease and prosthesis in patients with and without AF/flutter.




No comments yet!