Balloon- vs self-expanding valve systems for failed small surgical aortic valve bioprostheses
Selected in JACC : Journal of the American College of Cardiology by E. Zancanaro
Edoardo provides us with the cardiac surgeon's point of view!
The present trial aimed to clarify the hemodynamic results between balloon-expandable valve (BEV) (SAPIEN 3 ULTRA - Edwards) and self-expandable valve (SEV) (EVOLUT R/Pro/Pro+ - Medtronic) in case of dysfunctional small-sized surgical bio-prosthesis.
References
Authors
Josep Rodés-Cabau, Amr E. Abbas, Vicenç Serra, Victoria Vilalta, Luis Nombela-Franco, Ander Regueiro, Karim M. Al-Azizi, Ayman Iskander, Lenard Conradi, Jessica Forcillo, Scott Lilly, Alvaro Calabuig, Eduard Fernandez-Nofrerias, Siamak Mohammadi, Vassili Panagides, Emilie Pelletier-Beaumont, and Philippe Pibarot
Reference
J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Aug, 80 (7) 681–693
Published
August 2022
Link
Read the abstractReviewer
My Comment
Why this study – the rationale/objective?
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) has been established in the last decades as a valid option in case of previous implanted surgical aortic valve dysfunction (valve-in-valve procedure [ViV]). Still, some concerns remained in the case of small surgical bio-prosthesis, since high post-procedural transvalvular gradient and severe prosthesis-patient mismatch (PPM) are two challenging complications.The present trial aimed to clarify the hemodynamic results between balloon-expandable valve (BEV) (SAPIEN 3 ULTRA - Edwards) and self-expandable valve (SEV) (EVOLUT R/Pro/Pro+ - Medtronic), in case of dysfunctional small-sized surgical bio-prosthesis.
How was it executed – the methodology?
The present study is a prospective randomized controlled trial conducted by 11 centers, in patients with SMALL failed surgical aortic valve (23/21 mm) that experienced ViV with either BEV or SEV.
Study Endpoint
- Valve Hemodynamics --> residual maximal and mean transvalvular gradient, severe PPM, moderate-severe aortic regurgitation.
- Clinical --> Death, stroke, serious bleeding, pacemaker implantation, myocardial infarction)
NB: particular attention in the valvular hemodynamic assessment has been considered to the difference between catheterization and echocardiographic measurements.
What is the main result?
A total of 102 patients were included and 98 underwent ViV-TAVR procedure (2 patients died before the procedure, and 2 patients were treated medically without intervention). 46 patients received a BEV (SAPIEN 3: n = 40; SAPIEN 3 ULTRA: n = 6), and 52 patients had SEV (Evolut R: n = 20, Evolut PRO: n = 31, Evolut PRO+: n = 1). In the BEV group, 11 and 35 patients received 20- and 23-mm valves, respectively. In the SEV group, 34 and 18 patients received 23- and 26-mm valves, respectively.
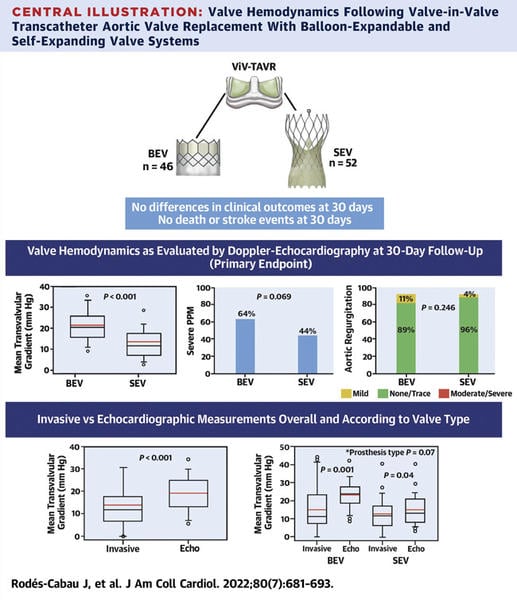
- ViV-TAVR with SEV (respect to BEV) was associated with improved valve hemodynamics considering transvalvular gradient -> 15±8 and 23±8 mm Hg for mean gradient, P < 0.001, respectively // 28±6 and 40±13 mmHg for maximal gradient, P < 0.001, respectively.
- ViV-TAVR with SEV (respect to BEV) was associated with improved valve hemodynamics considering PPM -> (64% vs 44%; P = 0.07).
NB: interestingly enough, there were no differences between groups in the mean transvalvular gradient following ViV-TAVR if measured by catheterization.
- ViV-TAVR was associated with a very low rate of peri-procedural and 30-day complications, with no cases of death or stroke in both the SEV and BEV groups.
Central illustration: Valve Hemodynamics Following Valve-in-Valve Transcathter Aortic Valve Replacement With Balloon-Expandable and Self-Expanding Valve Systems - Source : JACC
Critical reading and relevance for clinical practice
The results of this study demonstrated the safety profile of ViV-TAVR in small failed aortic valve bio-prosthesis with no difference between TAVR valves.Interestingly enough, SEV showed a better hemodynamic performance in this cohort with respect to BEV in terms of residual gradient and PPM (as echocardiographic findings). Of notice, the same results are not corroborated by the catheterization measurements.Two considerations have to be made:
- The results have to be read with caution since the small cohort can introduce some bias as well as the very short terms follow-up. Of notice, the discrepancy in results between the two types of hemodynamic assessment has to be taken into consideration.
- In clinical practice, this trial may help in choosing a precise strategy in case of small degenerated valves since this represents an evolving problem that we are facing with more frequency.
In conclusion, ViV-TAVR in small failed surgical bio-prostheses was associated with a very low rate of complications and 30-day adverse events. SEV provided improved hemodynamics as evaluated by echocardiography compared with BEV.





No comments yet!