RESHAPE-HF2 - Percutaneous repair of moderate-to-severe or severe functional mitral regurgitation in patients with symptomatic heart failure
Reported from ESC Congress 2024
Nicola Ryan provides her take on the RESHAPE-HF2 trial presented by Stefan Anker at the ESC Congress 2024 in London and simultaneously published in the NEJM.
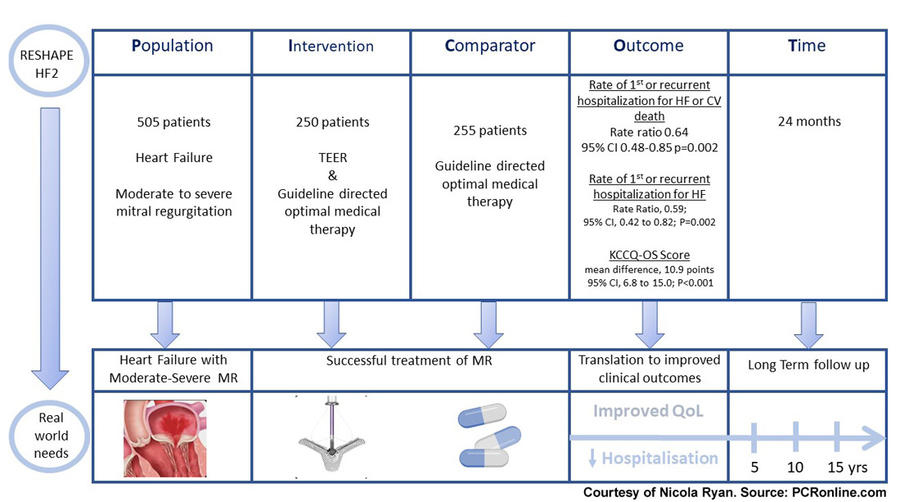
The RESHAPE-HF 2 trial is a prospective randomised control trial comparing transcatheter mitral valve repair (TEER) and guideline-directed medical therapy to guideline-directed medical therapy in patients with heart failure and moderate to severe functional mitral regurgitation.
PICOT analysis of RESHAPE-HF2. Courtesy of Nicola Ryan. Source: PCRonline.com
Why this study – the rationale/objective?
Despite optimal medical therapy, functional MR remains a significant problem in many patients with heart failure and is associated with a worse prognosis. Surgical mitral valve repair or replacement is not recommended in isolated functional severe MR. To date, trials of TEER in patients with severe MR and heart failure have demonstrated discordant results. In the COAPT trial, TEER led to a reduction in heart failure hospitalisations and all-cause death compared to medical therapy alone at two years. Conversely, the MITRA-FR trial did not show any differences in all cause death or heart failure hospitalisation with TEER and optimal medical therapy compared to optimal medical therapy alone at two years. It has been hypothesised that differing medical therapy, mechanisms of MR and severity of heart failure in the trials may explain the differing results. Furthermore, registry data suggests that approximately 44% of patients undergoing TEER have moderate rather than severe MR. On this background, the RESHAPE-HF2 trial was designed to assess the benefit of TEER in patients with heart failure and moderate to severe functional MR.
How was it executed - the methodology?
Patients with signs and symptoms of heart failure on optimal medical therapy with grade 3+ or 4+ functional MR and an EF of 20-50% were eligible for inclusion if they had a hospitalisation for heart failure or a BNP >300pg/ml or NT-pro BNP > 1000pg/ml within 90 days of randomisation. European Association of Echocardiography criteria were used to classify MR. Patients were randomised 1:1 to TEER and guideline-directed medical therapy or guideline-directed medical therapy alone.
- There were three primary endpoints
- The rate of the composite of first or recurrent hospitalisation for heart failure or death from cardiovascular causes during 24 months.
- The rate of first or recurrent hospitalisation for heart failure during 24 months
- The change from baseline to 12 months in the score on the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire- Overall Summary (KCCQ-OS)
- Secondary endpoints included MR of grade 2+ or worse at 12 months, change from baseline to 12 months in the 6-minute walking distance, death from any cause during the entire trial period, the rate of recurrent hospitalisation for any cause during 24 months, and NYHA functional class I or II heart failure at 12 months.
What is the main result?
Overall, 505 patients were enrolled in the RESHAPE-HF2 trial with 250 randomised to TEER, a device was successfully deployed in 244 of the 248 patients in whom it was attempted. ME f 1+ or lower was achieved in 74.5% of patients and 2+ in a further 17.7%. The majority of patients were male with a mean age of 80 years, 60% of patients were NYHA III at baseline with quarter NYHA II. Two-thirds of patients had been hospitalised for heart failure within the last year with a median EF of 32% and 44% of patients had grade 4+ MR.
- The rate of first or recurrent hospitalisation for heart failure or death from any cause was 37.0 events/100 patient-years in the TEER group versus 58.9 events/100 patient-years in the medical therapy group, rate ratio 0.64, 95%CI 0.48-0.85, p=0.002 during 24 months.
- The rate of first or recurrent hospitalisation for heart failure was 26.9 events/100 patient-years versus 46.6 events/100 patient-years, rate ratio 0.59, 95%CI 0.42-0.82, p=0.002.
- The mean change from baseline to 12 months in the KCCQ-OS score was 21.6±26.9 points in the TEER group versus 8.0±24.5 points least-squares mean difference, 10.9 points 95% CI, 6.8 to 15.0; P<0.001.
- 90.4% of the TEER group versus 36.1% of the medical therapy group have Grade 2+ or lower MR at 12 months.
Critical reading and the relevance for clinical practice
The results of this study show that in patients with symptomatic heart failure and moderate to severe or severe functional MR, TEER leads to a reduction in the composite rates of first or recurrent hospitalisation for heart failure or all-cause death and rates of first or recurrent hospitalisation for heart failure during 24 months. There was a larger increase in KCCQ-OS score at 12 months with TEER.
Different to both the COAPT and MITRA-FR trials the mean EROA was smaller (0.25cm2) at baseline reflecting the inclusion of patients with moderate to severe MR. Given that LV damage has been proposed as a predictor of benefit from TEER targeting patients prior to irreversible LV damage Is a potentially attractive strategy.
In the RESHAPE-HF2 trial, there was no reduction in all-cause death with TEER perhaps reflecting the overall health status of the population enrolled compared to The COAPT population. Reflective of the enrolment period there was relatively low utilisation of SGLT-2 inhibitors with <10% of patients on treatment at baseline. Current guideline-directed medical therapy recommends the use of SGLT-2 inhibitors in all heart failure patients without a contraindication. Similarly, due to the eight-year enrollment period differing generations of the TEER device were utilised depending on enrollment period, whilst not analysed in this study, it will be interesting to understand the longer term follow-up of patients by device type.
Overall this trial suggests that TEER is beneficial in terms of reducing hospitalisations for heart failure and the composite of heart failure hospitalisation and all-cause death as well as improving patient symptoms in patients with heart failure and grade 3+ or 4+ functional MR. The longer-term follow-up of this population will be of interest particularly to understand if treating functional MR at an earlier stage impacts clinical outcomes compared to LV modifying drugs alone.
Related publications
- Outcomes of transcatheter edge-to-edge repair for atrial functional mitral regurgitation
- Evolving indications for transcatheter mitral edge-to-edge repair
- Mitral valve transcatheter edge-to-edge repair
Latest news from ESC Congress 2024




No comments yet!